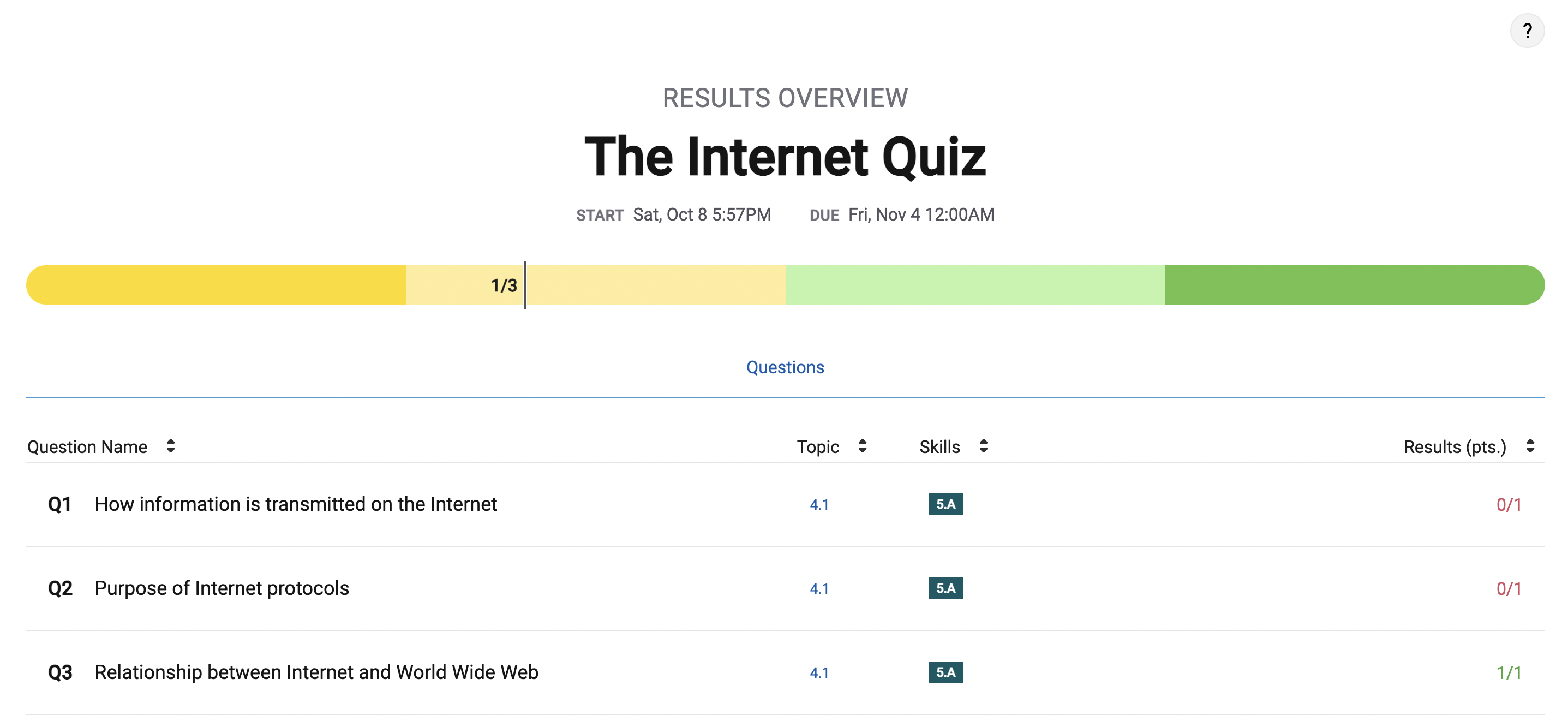
4.1 The Internet College Board Notes
My notes for big idea 4.1 college board videos.
Video 1
- A computing device: a physical artifact that can run a program.
- examples: computers, tablets, severs, routers, and smart sensors
- computing system: group of computing devices and programs working together for a common purpose
- computer network: group of interconnected computing devices that are capable of sending+recving data.
- a type of computing system
- path b/w two computing devices on a network
- sender
- reciver
- routing: the process of finding a path from sender to reciver
- bandwidth of a computer network: max amount of data that can be sent in a fixed amount of time
- meaured in bits per second
- packet: is a small amount of data sent over a network, includes the source and destination
Video 2
- the internet: a computer network with interconnected networks that sue open comminications protocols
- access to internet depends on ability to connect computing device to an internet connected device
- a protocol is an agreed-upon set of rules that specify the behavior of a system
- routing on the internet is usually dynamic, not specificed in advance
- the scalabitlity of a system is the capacity for the system to change in size and scale to meet new demands
- the internet was designed to be scalable
- information is passed through the internet as a data stream, data streams contain chunks of data, which are encapsulated in packets
- packets contain a chunck of data and metadata used for routing the packet between the orgin and the destination on the internet, as well as for data reassembly
- packets may arrive at the destination in order, out of order, or not at all
- IP, TCP, and UDP are common protocols used on the internet
- the world wide web is a system of linked pages, programs, and riles
- HTTP is a protocol used by the world wide web.
- the world wide web uses the internet
MC Completion